Internal Sensors
Light Sensor
The Senquip ORB is equipped with an internal light sensor that is used to activate the ORB setup functions when the lid is opened and to detect tamper attempts. The light sensor is sampled on a regular basis and does not have an associated measurement interval.
An alert can be generated when the ORB detects light, meaning that the lid has been opened.
Note
A tamper alert, if enabled will be triggered by a tamper attempt or an authorised entry to change settings.
A full list of light sensor settings is given in the table at the end of the chapter.
Accelerometer
The Senquip ORB has an integrated 3-axis accelerometer. The accelerometer allows for angle measurement, movement detection, harsh-usage monitoring and utilisation calculation. To provide more accurate measurement for pitch, roll and angle measurement, each time the accelerometer is measured, 10 samples will be taken at 1 msec intervals and the average will be returned as the measured value. Pitch, roll and angle will be calculated from the average acceleration.
Raw accelerometer data in the X (through the lid), Y (left to right across the ORB lid) and Z (from the hinge down to the cable gland) are available and are delivered in G’s. These values can be useful, for instance where an incident is being re-created from force data.
Note
Incident recreation using force data requires high speed sampling. Please contact Senquip to discuss your application.
When looking at the front cover, positive pitch is described as the top of the ORB tilting towards the observer. In the same scenario, negative pitch is described as the top of the ORB cover moving away from the observer.
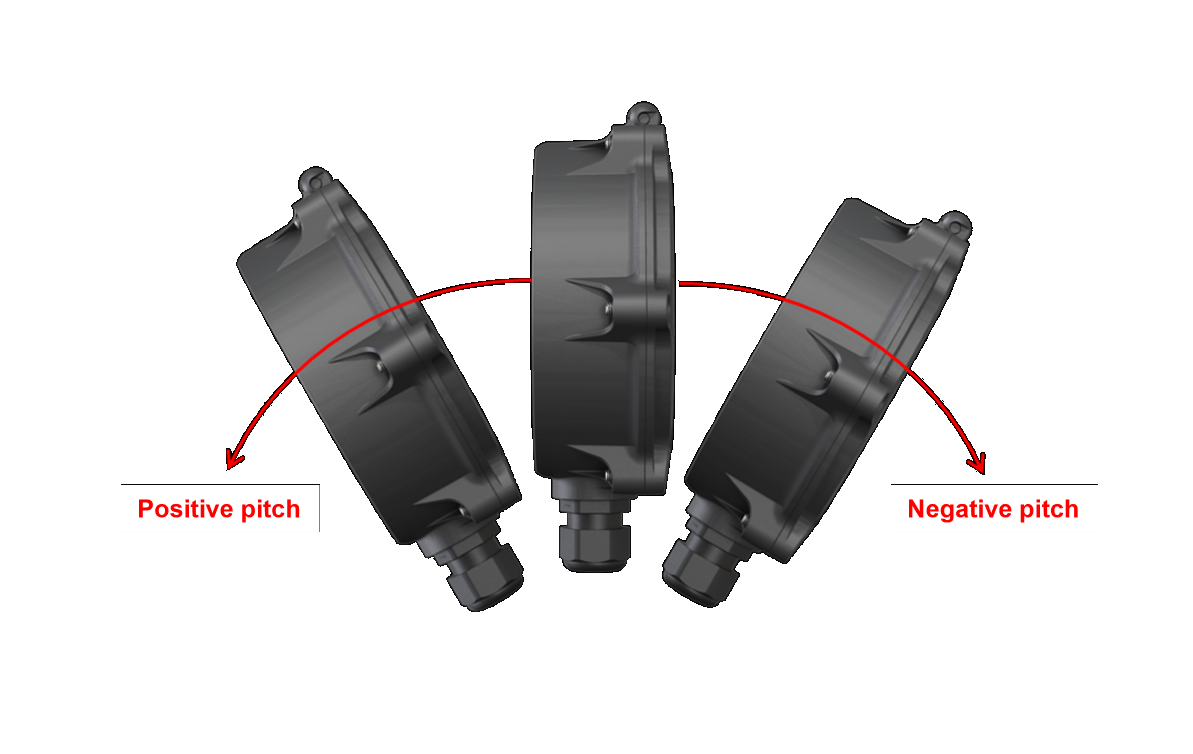
Definition of pitch
When looking at the front cover, positive roll is described as the top of the ORB tilting towards the right. In the same scenario, negative roll is described as the top of the ORB cover moving towards the left.
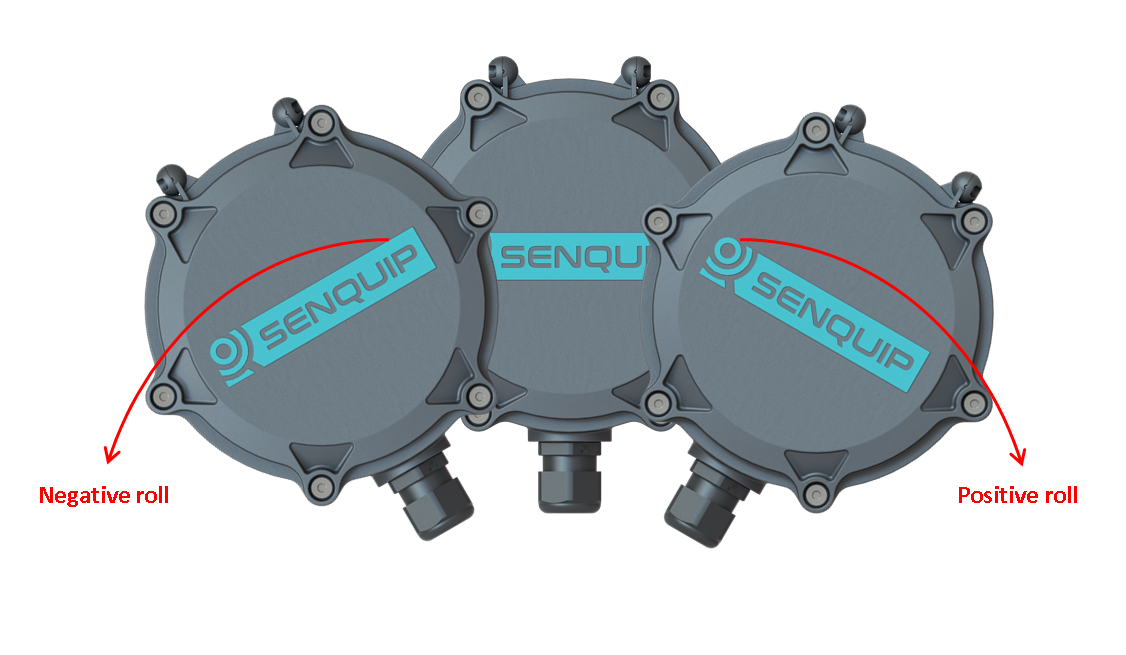
Definition of roll
Pitch and roll are useful in applications where objects to which the ORB is attached have a definite front, back, left and right; for instance a vehicle. For objects like a pole, the user may be more interested in the angle of the pole to vertical. In these applications, the tilt may be more useful than pitch or roll.

Definition of tilt
Specification
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
G-force range |
+- 16G |
Resolution |
1mG |
Sensitivity change vs temperature |
0.1% per°C |
Typical zero-g level offset accuracy |
+- 40mG |
Tilt resolution |
0.1 deg |
Tilt accuracy (0-45 deg) |
1.0 deg |
Tilt accuracy (45-90 deg) |
2.0 deg |
Settings
Accelerometer measurements can be scheduled as a multiple of the base-interval. The fastest possible measurement rate is achieved by setting the interval to 1 in which case measurements will occur on every base interval. To reduce power consumption, the measurement rate can be turned down by increasing the interval.
Warning and alarm thresholds for pitch, roll and angle can be enabled. Once enabled, each time a measurement is completed, the returned value will be compared with minimum and maximum warning and alarm thresholds. If a warning or alarm level is breached, a message will immediately be transmitted. As long as the warning or alarm condition persists, messages will be transmitted at the exception-interval rather than the transmit-interval. Hysteresis can be specified in 1 degree increments, to prevent multiple alarms in the presence of vibration.
The accelerometer is able to detect motion and shocks due to harsh usage even during sleep. If motion or shock monitoring is enabled and either of those events occurs, a flag will be set. Event flags are checked at each base-interval and if one exists, an alert message can be scheduled to be sent at that time. The threshold as well as time for which an activity must be present can be set for both motion and shock monitoring.
Note
Pitch and roll warning and alarm levels can be positive or negative. Angle warning and alarms can only be positive.
Vibration can be used as a trigger to count hours. This may be useful where the number of hours that an engine is running needs to be calculated.
A full list of accelerometer settings is given in the table at the end of the chapter.
Magnetic switch
The Senquip QUAD contains a built-in hall-effect sensor that acts as a magnetic switch. When the switch detects a magnet, the Senquip QUAD can be made to enter setup mode, wakeup, or trigger a function in a script.
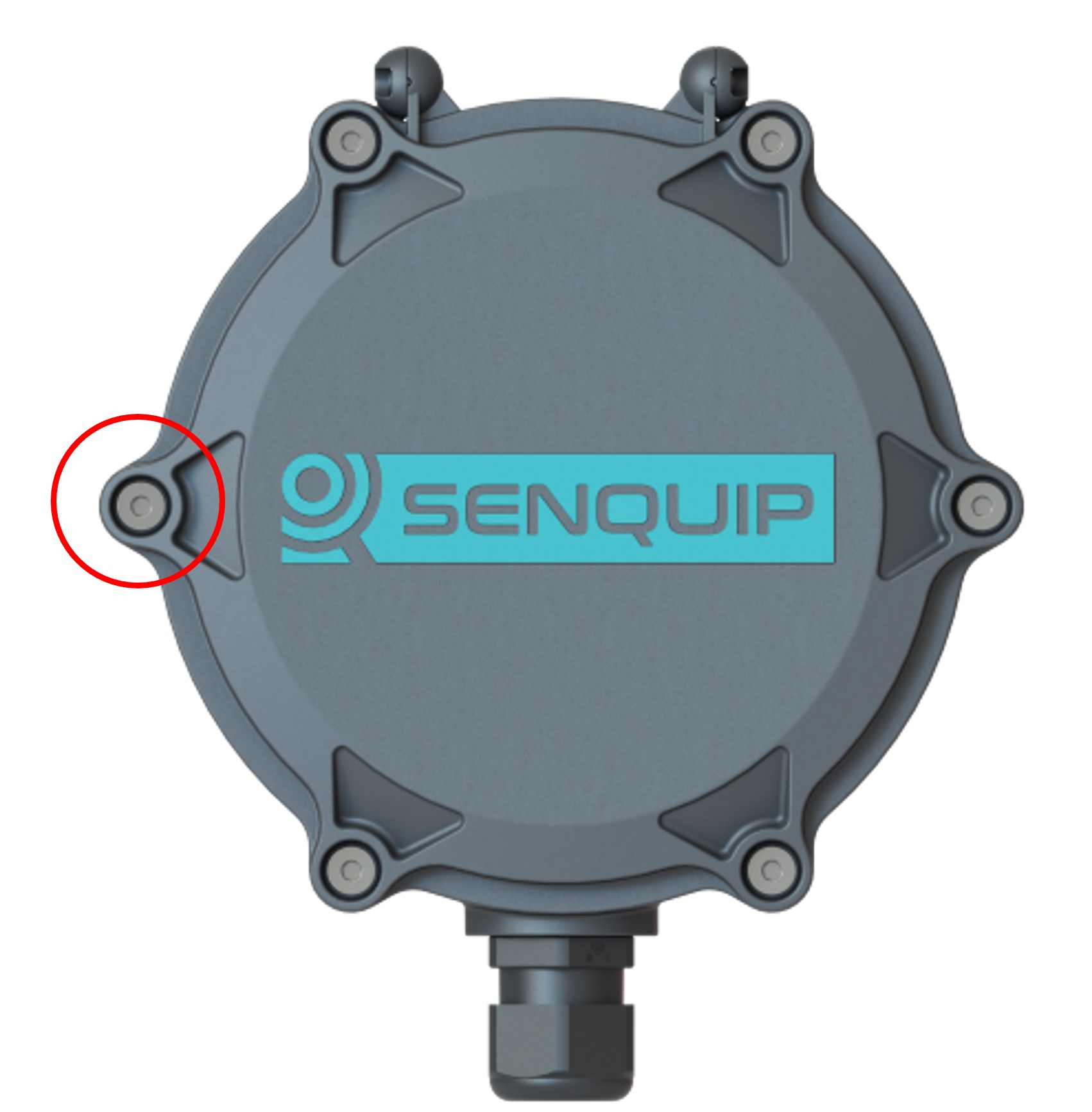
Location of magnetic switch
Settings
Three actions are available when the magnetic switch is activated.
Setup: Put the device into setup mode. Identical to pressing the Setup button. If the device is asleep, it will wake and enter Setup Mode.
Wake: Wake the device up and perform a measurement cycle. There is no action if device is already awake.
Trigger: Wake the device if asleep. Trigger TP0 before first measurement cycle. TP0 should be handled in a script.
Temperature sensor
An integrated temperature sensor allows for measurement of ambient temperature. Please be aware that the temperature sensor will measure the temperature inside the ORB enclosure; this temperature can be subject to fluctuations, for example when the internal lithium ion battery is charging and so the environment within the ORB heats up. For accurate external temperature measurement or to measure a wider range of temperatures, use the thermocouple peripheral.
Specification
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
Measurement range |
-40 - 85°C |
Resolution |
0.01 deg°C |
Absolute accuracy (25°C) |
+-0.5 deg°C |
Absolute accuracy (0 - 65°C) |
+-1 deg°C |
Settings
Measurements can be scheduled as a multiple of the base-interval. The fastest possible measurement rate is achieved by setting the interval to 1 in which case measurements will occur on every base interval. To reduce power consumption, the measurement rate can be turned down by increasing the interval.
Warning and alarm thresholds for ambient temperature can be enabled. Once enabled, each time a measurement is completed, the returned value will be compared with minimum and maximum warning and alarm thresholds. If a warning or alarm level is breached, a message will immediately be transmitted. As long as the warning or alarm condition persists, messages will be transmitted at the exception-interval rather than the transmit-interval. Hysteresis can be specified in 1°C increments, to prevent multiple alarms in the presence of fluctuating temperature.
A full list of temperature sensor settings is given in the table at the end of the chapter.
GPS
Models of the ORB that have 4G LTE connectivity also have an integrated Global Positioning System (GPS). The GPS receiver, with integrated antenna and LNA allows for position and speed based reporting. The internal GPS will receive GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou and Galileo satellites to ensure high accuracy measurement and fast time to first fix. Data available from the GPS includes:
Latitude, longitude and height
Speed (km/h) and bearing
Date and time
Number satellites being tracked
In order to utilise the GPS, the ORB needs to be mounted such that the internal antenna has visibility of the sky. Plastic and fibreglass roof sheeting will have a minimal effect on GPS performance whereas reinforced concrete and metal roofs will render the GPS inoperable. In applications where GPS is required but the ORB cannot be mounted in a position where the sky is visible, a GPS re-radiating antenna can be used. Please make sure that the chosen re-radiating antenna is of high quality and legal for use in your region. An advantage of good GPS signal quality is that the ORB will consume less power as acquisition time will be less.
Specification
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
Time to first fix from power up |
Typically 60 seconds |
Position update rate |
Maximum 1Hz |
Horizontal position accuracy |
Typically +-5m (<2.5m CEP-50) |
Vertical position accuracy |
Typically +-20m |
Horizontal speed accuracy |
1km/h |
Settings
Measurements can be scheduled as a multiple of the base-interval. The fastest possible measurement rate is achieved by setting the interval to 1 in which case measurements will occur on every base interval. To reduce power consumption, the measurement rate can be turned down by increasing the interval. The GPS is a high power peripheral and so use should be limited when running on battery power.
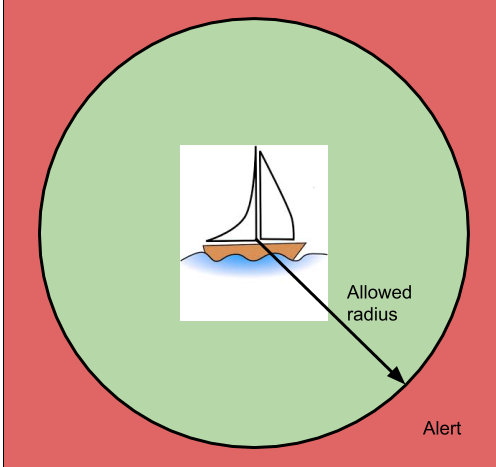
GPS alert parameters
The GPS can create an alert based on position and speed. A known position (expected latitude and expected longitude) can be specified and if the ORB moves a particular radius from that point, an alert can be raised. Hysteresis can be specified in 1 meter increments to prevent multiple alerts, for instance as a boat swings on a mooring near the edge of the allowed radius. Likewise, a maximum speed can be specified and if the ORB exceeds that speed, an alert will also be raised. Speed hysteresis can be specified in 1km/h increments, to prevent multiple alerts as the speed fluctuates at the alert point. The time that GPS speed exceeds 2km/h can counted and be used to calculate machine utilisation.
Note
In the example above, the ORB could also report bilge water level, solar battery voltage and a host of other parameters associated with the yacht.
A full list of GPS settings is given in the table at the end of the chapter.
Bluetooth Interface
The ORB has a Bluetooth peripheral that can transmit and receive Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) advertising packets. BLE beacons typically use the advertising packets to communicate measured data such as temperatures, voltages, movement, and battery voltage. BLE tags are a special type of beacon that typically only contain identification information and are used to locate items. BLE beacons send advertising messages at different rates. Some report every second and some may be every minute or more. Battery operated BLE devices tend to send at lower rates to save power. Some BLE device are smart and will slow their send rate if they are not being used. A tire pressure monitoring device may stop sending if the tire is not rotating. Typical protocols used in advertising packets include Eddystone and iBeacon. The ORB supports both.
The BLE beacons from ELA shown below enable identification, and measurement of temperature, humidity, voltage, switch position, and more.
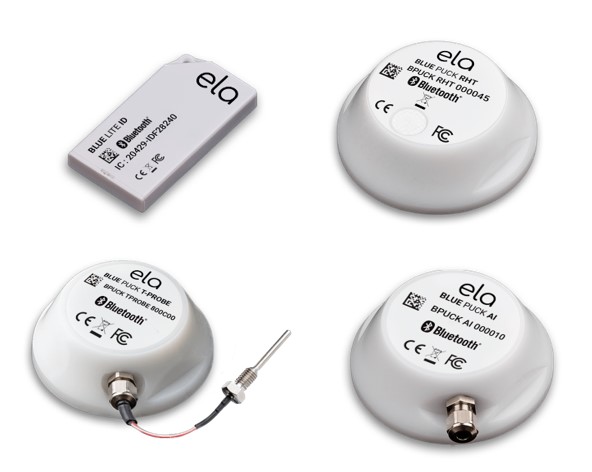

Example BLE beacons from ELA
The ORB will report the beacon address, data, and the strength of the received signal.
The address (or identifier) is unique and allows individual tags to be recognised.
The data may contain battery voltage, temperature, humidity, or any other data being conveyed by the beacon.
The receive signal strength (RSSI) gives an indication of how strong the signal from the beacon is.
For details on using the ORB as a BLE beacon to transmit custom advertising packets, please refer to the Senquip Scripting Guide.
Note
The BLE module and Wi-Fi module share a common radio. BLE operation will work best when the ORB is operated using a cellular network rather than Wi-Fi.
Specification
Parameter |
Specification |
|---|---|
Bluetooth version |
4.2 |
Settings
Measurements can be scheduled as a multiple of the base-interval. The fastest possible measurement rate is achieved by setting the interval to 1 in which case the Bluetooth peripheral will be sampled on every base interval. To reduce power consumption, the measurement rate can be turned down by increasing the interval.
When active, the Bluetooth peripheral will scan for all advertising packets. In a typical environment, phones, computers, and other devices are all advertising. The ORB Bluetooth peripheral could easily report a dozen Bluetooth devices even when the one you are searching for is off. The ORB can filter for only the required Bluetooth devices by filling in the Address Capture List. Required addresses should be entered in hexadecimal and should be separated by commas. When the ORB wakes for the next measurement interval, the Bluetooth peripheral will be sampled until all the messages listed have been found or the Capture Time has been reached. If multiple messages with the same identifier are required in a single measurement interval, place a * followed by the number of messages of that identifier to be returned after the identifier in the list. For example: 98588A10375E*4, 98588a103777, 98588a103888*10 will return 98588A10375E four times, 98588a103777 once and 98588a103888 ten times. Leave the ID Capture List blank to receive all messages.
The Capture Time setting can be used to set a timeout after which the Bluetooth peripheral will stop listening, allowing the ORB to transmit received messages and return to sleep. Capture-time can be used as a mechanism to allow the ORB to sample the environment for devices for a defined time-period.
A full list of Bluetooth settings is given in the table at the end of this chapter.
Internal Sensor Settings
A full list of settings for internal sensors is given in the table below.
Name |
Item |
Function |
Range |
Unit |
Internal Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Light Sensor |
|||||
Name |
text |
A name for the light sensor that is meaningful to the user. |
25 chars |
tamper.name |
|
Tamper Alert |
boolean |
This parameter determines if an alert is generated when the light sensor detects light or not. |
tamper.enable |
||
Ambient Temperature |
|||||
Name |
text |
A name for the input that is meaningful to the user. |
25 chars |
ambient.name |
|
Interval |
integer |
The number of base intervals after which the temperature is sampled. A value of 1 means that the input is collected every base interval. Set to 0 to disable. |
0 to 10000 |
ambient.interval |
|
Hysteresis |
decimal |
The amount by which the measured value has to drop below the threshold to re-enable the alert after an event. |
0 to 100 |
°C |
ambient.hysteresis |
Warning |
text |
Warning thresholds. Refer to user guide. |
-40 to 100 |
°C |
ambient.warning |
Alarm |
text |
Alarm thresholds. Refer to user guide. |
-40 to 100 |
°C |
ambient.alarm |
Accelerometer |
|||||
Name |
text |
A name for the input that is meaningful to the user. |
25 chars |
accel.name |
|
Interval |
integer |
The number of base intervals after which the accelerometer is sampled. A value of 1 means that the input is collected every base interval. Set to 0 to disable. |
0 to 10000 |
accel.interval |
|
Output XYZ Vectors |
boolean |
Send X,Y,Z gravity vectors in data output. |
accel.outputxyz |
||
Hysteresis |
decimal |
The amount by which the pitch, roll or angle has to exceed a threshold before triggering alarms or warnings. |
0 to 20 |
Degrees |
accel.hysteresis |
Pitch Warning |
text |
Warning thresholds. Refer to user guide. |
-90 to 90 |
Degrees |
accel.pitch.warning |
Pitch Alarm |
text |
Alarm thresholds. Refer to user guide. |
-90 to 90 |
Degrees |
accel.pitch.alarm |
Roll Warning |
text |
Warning thresholds. Refer to user guide. |
-90 to 90 |
Degrees |
accel.roll.warning |
Roll Alarm |
text |
Alarm thresholds. Refer to user guide. |
-90 to 90 |
Degrees |
accel.roll.alarm |
Angle Warning |
text |
Warning thresholds. Refer to user guide. |
0 to 90 |
Degrees |
accel.angle.warning |
Angle Alarm |
text |
Alarm thresholds. Refer to user guide. |
0 to 90 |
Degrees |
accel.angle.alarm |
Motion Warning |
text |
Warning thresholds. Refer to user guide. |
0 to 5000 |
milli-g |
accel.motion.warning |
Motion Alarm |
text |
Alarm thresholds. Refer to user guide. |
0 to 5000 |
milli-g |
accel.motion.alarm |
Wake from Hibernate |
boolean |
The high warning motion threshold is used to wake the device when hibernating. |
accel.motion.wake_from_hibernate |
||
Motion Wake Threshold |
decimal |
The motion threshold above which the device will wake from hibernation. |
1 to 2000 |
milli-g |
accel.motion.wake_threshold |
Count Motion Hours |
boolean |
Counts the number of hours the device exceeds the Motion Wake Threshold. Typically used as an machinery work vs idle hour meter. |
accel.motion.count_hours |
||
GPS |
|||||
Name |
text |
A name for the GPS signal that is meaningful to the user. |
25 chars |
gps.name |
|
Interval |
integer |
The number of base intervals after which the gps is sampled. A value of 1 means that the input is collected every base interval. Set to 0 to disable. |
0 to 10000 |
gps.interval |
|
Max Time |
integer |
Maximum time the device will wait for a valid GPS fix. |
0 to 3600 |
Seconds |
gps.maxtime |
Position |
|||||
Position Alert |
boolean |
Sets whether a change in position generates an alert. |
gps.position.alert.enable |
||
Radius |
integer |
An alert will be raised if the device moves further than this value from the expected position. |
1 to 10000 |
Meters |
gps.position.alert.radius |
Hysteresis |
integer |
Once the alert is active or inactive, the radius must change by this value to change the alert state. |
1 to 10000 |
Meters |
gps.position.alert.hysteresis |
Expected Latitude |
decimal |
Latitude at which the device is expected to be. |
-90 to 90 |
Degrees |
gps.position.alert.lat |
Expected Longitude |
decimal |
Longitude at which the device is expected to be. |
-180 to 180 |
Degrees |
gps.position.alert.lon |
Speed |
|||||
Count Movement Hours |
boolean |
Counts the number of hours the device is moving according to the GPS speed. |
gps.speed.count_hours |
||
Speed Alert |
boolean |
Sets whether a change in speed generates an alert. |
gps.speed.alert.enable |
||
Threshold |
integer |
An alert will be raised if the device’s speed goes above this threshold. |
1 to 1000 |
km/h |
gps.speed.alert.threshold |
Hysteresis |
integer |
Once the alert is active or inactive, the speed must change by this value to change the alert state. |
1 to 1000 |
km/h |
gps.speed.alert.hysteresis |
Bluetooth |
|||||
Name |
text |
A name that is meaningful to the user. |
25 chars |
ble.name |
|
Interval |
integer |
The number of base intervals after which the Bluetooth module is turned on. Set to 0 to disable. |
0 to 10000 |
ble.interval |
|
Scan Time |
integer |
The device will capture matching messages for this length of time. |
Seconds |
ble.capture_time |
|
Address Capture List |
text |
List of adresses to be captured in HEX format, separated by a comma. Leave blank to capture all. |
200 chars |
ble.id_list |
|
Send Raw Data |
boolean |
If ticked, all captured messages will be added to the data message. |